Erratum to: The Journal of Aging Research & Lifestyle DOI 10.14283/jarlife.2023.13
P.M. Doraiswamy1,2,3, M.G. Miller2, C.A. Hellegers1, A. Nwosu1, J. Choe4, D.M. Murdoch4
1. Neurocognitive Disorders Program, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Sciences, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA; 2. Duke Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA; 3. Duke Institute for Brain Sciences, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA; 4. Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA
Corresponding Author: P. Murali Doraiswamy, Neurocognitive Disorders Program, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Sciences, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, USA, murali.doraiswamy@duke.edu
J Aging Res & Lifestyle 2023;12:84
Published online September 25, 2023, http://dx.doi.org/10.14283/jarlife.2023.14
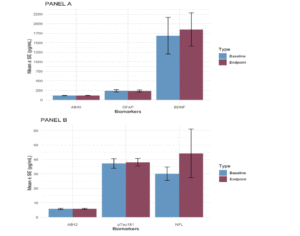
The authors from «Blueberry Supplementation Effects on Neuronal and Pathological Biomarkers in Subjects at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pilot Study”, J Aging Res & Lifestyle 2023;12:77-83, advise an error in Figure 2. The original Figure 2 has been corrected to display the corect SE bars.
Figure 2A and Figure 2B depict mean (SE) plasma biomarker values at baseline (depicted in blue) and week 12/endpoint (depicted in purple). There were no statistically significant differences for any of the biomarkers measured. Abbreviations: Aβ40 = amyloid-beta 40; Aβ42 = amyloid-beta 42; ptau181 = phosphorylated Tau181; NfL = neurofilament light; GFAP = Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein; BDNF = Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor
© The Authors 2023